- 一个bound的service是C/S的接口。它允许其他组件绑定到service,发送请求,接收回应并执行IPC。通常是需要给其他程序组件提供服务。
- A bound service allows other components to bind to it, in order to interact with it and perform interprocess communication。
- A bound service is destroyed once all clients unbind, unless the service was also started。
- 客户端通过执行 bindService()绑定到service。这样的话,客户端需要实现一个ServiceConnection, 它可以监视与service的连接状态。bindService() 并不会有返回值,但是Android系统会在client与service连接上时,执行onServiceConnected() 的callback。在这个回调方法里面传递IBinder给client用来与service进行交互。
- 前面提到可以有多个Client同时bind到service。然而,系统只会在第一个client做绑定时才会执行service的onBind() 方法。对于随后需要绑定的客户端,系统会直接传递同一个 IBinder 对象给Client,而不是去再次执行onBind方法。(那么也就是onBind方法只会被执行一次)
- 通常来说,Music程序需要实现service的两种方式,这样既可以在activity被销毁之后(假设只实现bound的方式的话,这个时候,unbind了,Music会停止)音乐可以继续播放,当重新进入activity时又会重新bind上。这刚好验证了下面的说法:
- 如果一个service既可以started与bound。当一个service是started的,系统并不会在所有的Client都unbind之后去杀死这个service,我们需要显示的去停止这个service,通过stopSelf或者stopService的方式。
创建一个bound的Service
- 当创建了一个可以绑定的service之后,你必须提供一个IBinder对象,它用来提供client与service进行交互的接口。我们有下面三种方式来实现这个接口:
- Extending the Binder class: 如果你的sevice是私有的(不需要与其他程序进行IPC交互),Client可以与Service在同一个Process里面直接进行交互。若不需要IPC,建议使用这个方法。
- Using a Messenger: 可以使用handler与message进行IPC操作,这是一种直观简便的方式。一个发送消息,一个接受处理后并返回。Handler使得有一个Queue来装这些发送的请求,然后Service再逐个接受并进行处理。(这样的话,只能顺序执行那些发出的请求)
- Using AIDL(Android Interface Definition Language): 一种系统可以理解并做出合适处理的IPC机制。使用AIDL可以处理同时发出的请求(并发)。在这种情况下,Service必须小心仔细的去处理多线程操作。 我们需要生成一个.aidl的文件来定义接口,Android SDK tool会使用这个文件生成一个抽象类,在这个类里面去实现接口并处理IPC。
- 请注意:AIDL的方式并不常见,因为他实现起来更加复杂,若需要了解AIDL的详情,请参考后续文章。
(1)Extending the Binder class
Note: 这种方法仅仅适合client与service在同一个程序与process中的情况。这种情况是最常见的。例如,如果你的音乐程序需要bind到一个activity,并且想使得播放音乐在后台。(实际上,大多数情况下,播放音乐程序的service都需要与其他process的组件进行bind,所以这种方式extend Binder类的方式只适合简单的播放需求)
实现步骤
- In your service, create an instance of Binder that either:Return this instance of Binder from the onBind() callback method.
- contains public methods that the client can call
- returns the current Service instance, which has public methods the client can call
- or, returns an instance of another class hosted by the service with public methods the client can call
- Return this instance of Binder from the onBind() callback method.
- In the client, receive the Binder from the onServiceConnected() callback method and make calls to the bound service using the methods provided.
- In your service, create an instance of Binder that either:Return this instance of Binder from the onBind() callback method.
Service端代码示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | |
- Client端代码示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 | |
(2)Using a Messenger
- 这是避免使用AIDL仍然可以实现IPC的一个简便方法。
- Service实现一个Handler来接受Client的每一个callback。
- 这个Handler用来创建Messenger 对象。
- Messenger 创建一个IBinder对象,Service在onBind方法里面把这个对象返回给客户端。
- 客户端使用这个IBinder对象来实例化 Messenger (that references the service’s Handler), 然后客户端使用这个messager再发送message对象给service。
- Service在它的handler里面接收到每一个Message。
- Service代码示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | |
- Client端代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 | |
- 请注意:上面并没有演示Service接收到Client的Msg之后,如何再与Client进行交互的。如果想了解更多请看Demo Source Code:MessengerService.java (service) and MessengerServiceActivities.java (client) samples.
(3)AIDL:关于这部分内容,请看下一篇文章
- 使用Messager与AIDL的对比:
- 如果想要IPC,使用Messager要比AIDL更简单,只是AIDL可以处理并发的情况,更加复杂一点。
- 对于大多数App来说,都不需要处理多线程并发的问题,所以使用Messager会更简单一点。每次处理一个message。
- 如果你的Service需要是多线程的,那么需要使用AIDL。(有多个bind对象,他们可能会同时发出request)
绑定到Service
- 因为Binding的操作是异步(asynchronous)的, bindService() 会立即返回,并不携带IBinder对象返回给Client。为了接收到IBinder对象,客户端需要创建一个 ServiceConnection 来接收它。
- Note: 只有activities, services, and content providers 可以bind到service,你不可以从broadcast receiver里面去做bind service的操作。
- 为了实现Bind到Service,你需要做以下的事情:
- Implement ServiceConnection.需要重写下面两个方法
- onServiceConnected(): 系统会在connected上的时候call到这个方法。
- onServiceDisconnected(): 只有在serivce被异常终结时才会call到这个方法,正常的unbind不会call这里。
- 当系统call了onServiceConnected()之后,你可以开始使用定义好的接口去呼叫service。
- 想要与service解绑,可以执行 unbindService()。
- Implement ServiceConnection.需要重写下面两个方法
- Additional notes:
- 你应该总是去捕获 DeadObjectException ,当connection被破坏时会抛出这个异常。
- 对象都是跨process引用的。
- 你应该成对的使用bind与unbind。例如
- 如果你不想在activity不可见的时候再与service进行交互,需要在activity的onStart里面进行bind,在onStop里面去unbind。
- 如果想在activity不可见时,仍然进行交互,那么在onDestory里面再去做unbind。
- 请不要在activity的onResume与onPause里面去做bind与unbind,这两个activity的状态切换太频繁,不适合用来做与service的交互。
管理Bound Service的Lifecycle
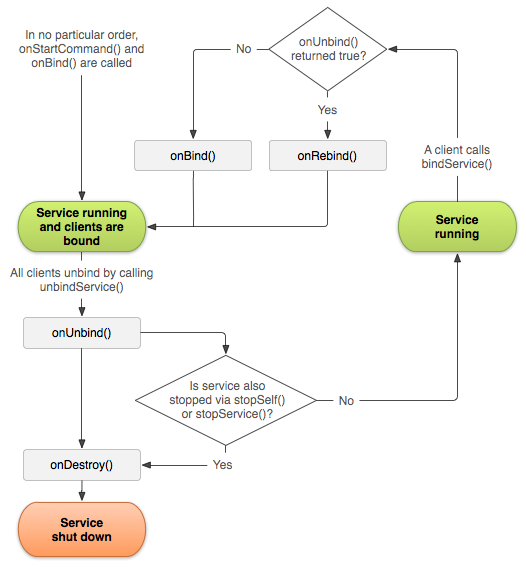
- 如果这个service是一个单纯的bound service(不是started与bound的混合体),那么Android系统会自动去管理它的lifecycle。(当所有的client都unbind时,系统kill这个service)。
- 如果你实现了onStartCommand()方法,那么这个service就被认为是started类型的,那么即使所有的client都unbind了,那么还是需要通过stopSelf或者stopService的方式来停止这个service。
- 另外,如果你的service是started类型的,并且还可以接受bind操作。那么当系统执行你的 onUnbind() 方法时,如果你想在Client下次bind上service的时候系统去call onRebind(而不是重新call onBind),你可以选择在onUnbind里面去return true。 在 onRebind() 会返回void,但是client仍然会在onServiceConnected里面接受到IBinder。
文章学习自http://developer.android.com/guide/components/bound-services.html
转载请注明出自http://kesenhoo.github.com,谢谢